Innovative Solution
Neoasis® is a non-contact device that can reduce noise levels in a space. It does this by broadcasting a cancelling sound wave in response to the analyzed sound environment. Using calculations performed in a few microseconds, the system determines the optimum sound wave at that moment needed to minimize the sound pressure level over the greatest area. Additionally, the system provides a means for a parent’s or caregiver’s voice to be transmitted into the incubator for critical directed communication with the infant without the interference of the incubator walls.
Publication Of Effectiveness In Simulated NICU Environment
Background
- Noise exposure in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) has been demonstrated to be consistently louder than the recommended guidelines of 45 dBA established by the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP).
- Various approaches have been attempted to address this noise problem; however, these attempts have not proven consistently effective.
- Single-family rooms are becoming more prevalent and have been shown to reduce noise levels, but still have average equivalent noise levels above AAP guidelines.
- NICU noise levels have been shown to impact the sleep hygiene of hospitalized infants and sleep is one of the most important behavioral states for neonates, particularly preterm neonates.
NICU noise levels have also been linked to slower growth rates for preterm patients. Poor growth in preterm infants is associated with worsened long-term outcomes, including impaired neurodevelopment.
Objectives
- While neonatal ear covers have been associated with improved weight gain and sleep hygiene, these ear covers are contraindicated and unreliable. We sought to determine if the Neoasis® can provide similar or better noise reduction without the drawbacks of the ear covers.
- We sought to quantify the noise reduction zone provided by the Neoasis®.
Methods
We evaluated a non-contact incubator-based active noise control device (Neoasis®, Invictus Medical, San Antonio, Texas) in a simulated neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) setting to determine whether it could effectively reduce the noise exposure of infants within an incubator. In the NICU simulation center, we generated a series of clinically appropriate sound sequences with bedside medical devices such as a patient monitor and fluid infusion devices, hospital air handling systems, and device mechanical sounds. A microphone-equipped infant manikin was oriented within an incubator. Measurements were made with the microphones with the Neoasis® deactivated and activated.
Test 1: Attenuation comparison with ear covers
For each sound sequence, sound pressure measurements were made at each manikin ear under four test conditions including (1) no noise reduction (control), (2) Neoasis®, (3) ear covers without hair, and (4) ear covers positioned on hair. The noise reduction provided by the Neoasis® and the ear covers with and without hair were calculated by subtracting those measured band levels from the control measurement band levels for each octave band.
Test 2: Noise reduction zone quantification
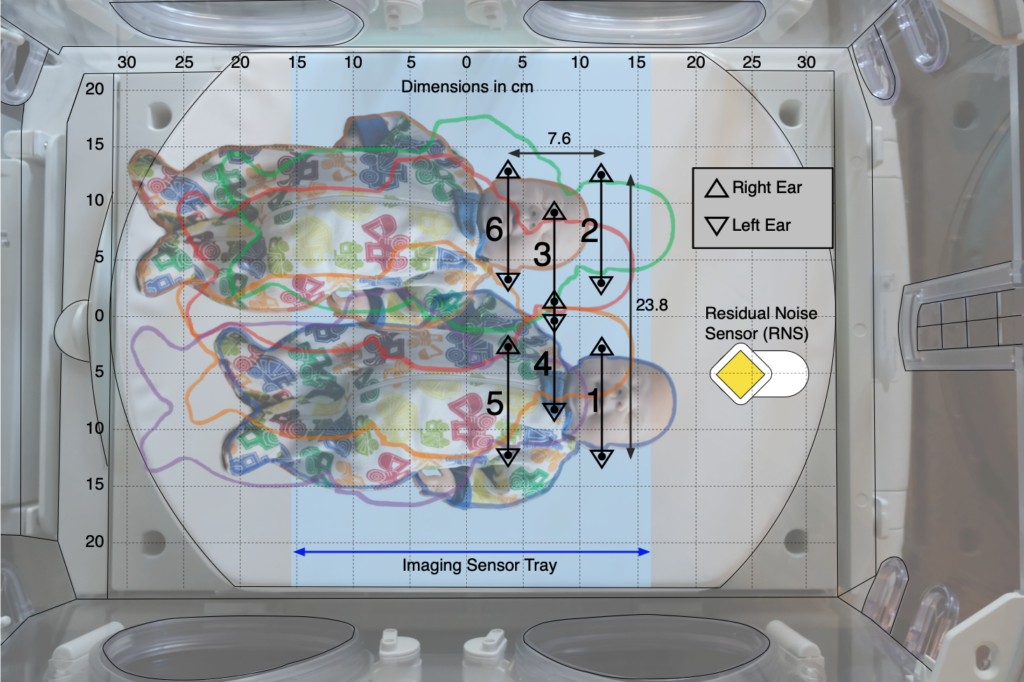
In the second of the two protocols, the effect of patient position on noise reduction efficiency was evaluated by measuring noise reduction at both ears of a manikin in six positions (see figure below) within an incubator with each sound sequence.
Results
Test 1: Attenuation comparison with ear covers
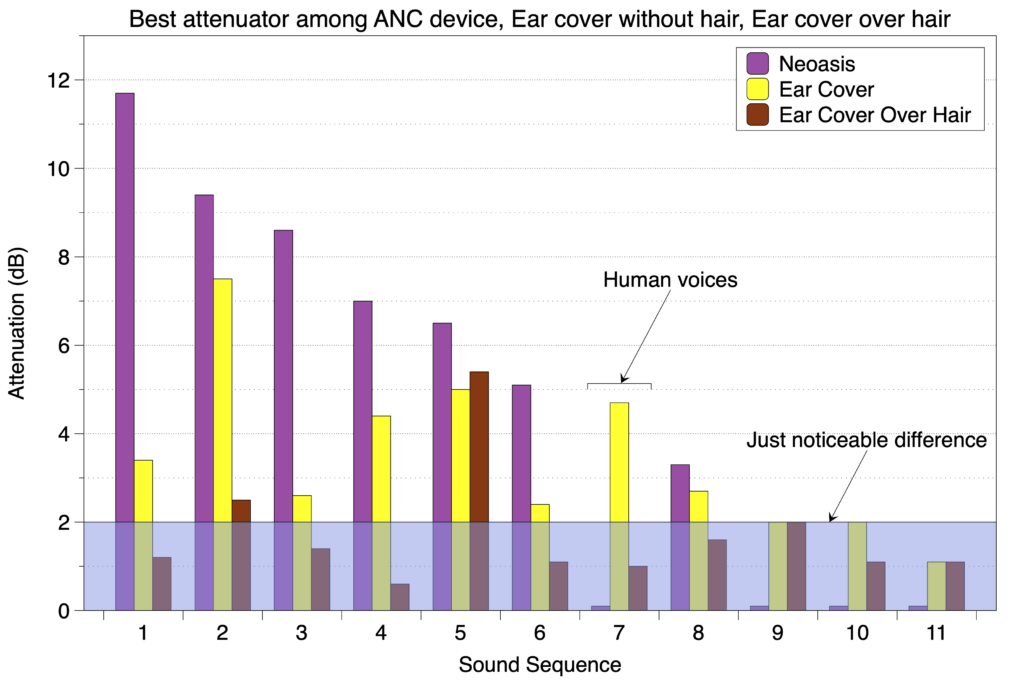
For every sound sequence tested where the attenuation among the different devices was greater than the just noticeable difference of 2 dB, the Neoasis® had the best attenuation. The one exception to this was for the sound sequence consisting of male and female voices, the one situation where exposure is actually good. This is shown in the graph below.
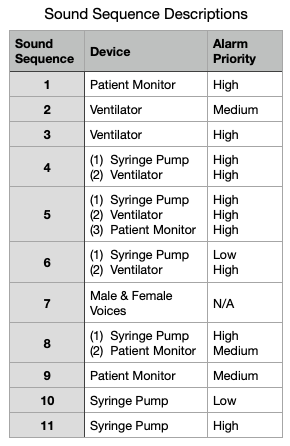
The description of the different alarms sequences is shown in this table.
Below the just noticeable difference, humans can’t distinguish between a 2 dB drop and a 0 dB drop.
Since attenuation is measured in dB (decibels), the scale is logarithmic so a drop of 10 dB is a 3-fold drop in the sound wave amplitude.
Test 2: Noise reduction zone quantification
We found that for frequencies in the 500 Hz octave band, the Neoasis® provided good attenuation no matter where the infant would be reasonably place in the incubator. For frequencies in the lower half of the 1 kHz, the Neoasis® provided good attenuation when the infant is placed according the user’s manual.
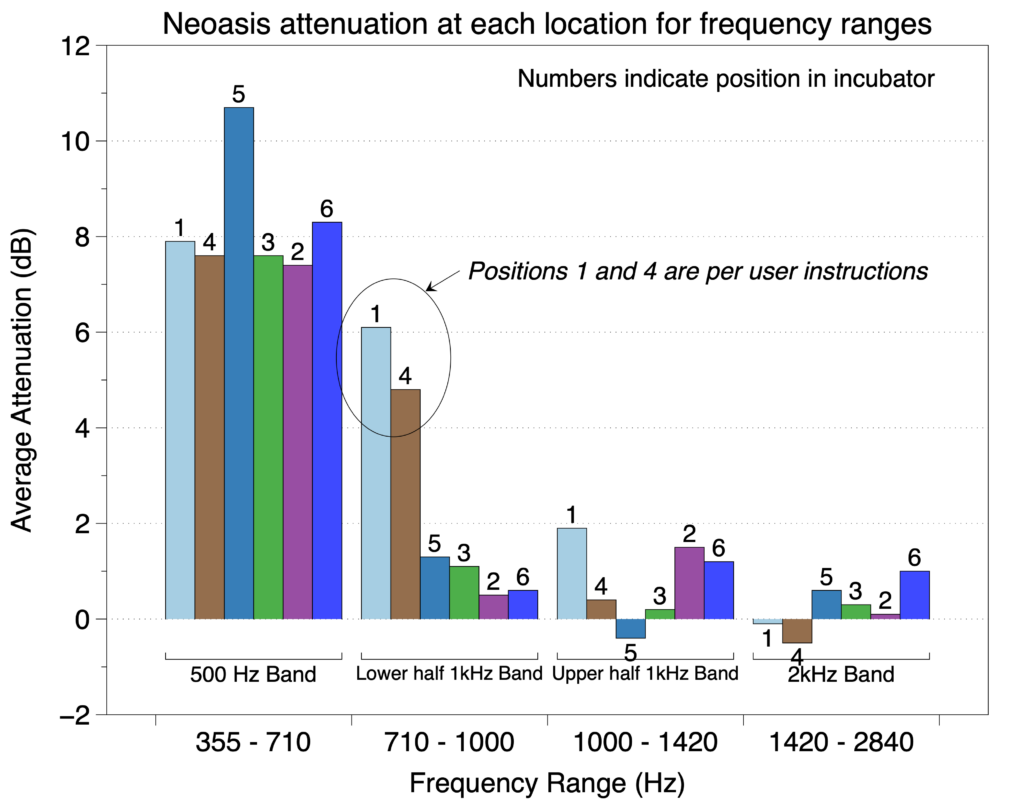
The preponderance of alarm frequencies found in NICUs are in the 500 Hz band.
Conclusions
The Neoasis provided superior noise reduction to the ear covers in this simulated environment test for all alarm sounds where the noise reduction difference was greater than the just noticeable difference. These simulation results demonstrate for the first time, in principle, the ability to successfully utilize active noise cancellation in the NICU setting to reduce environmental noise exposure.
Components Of System
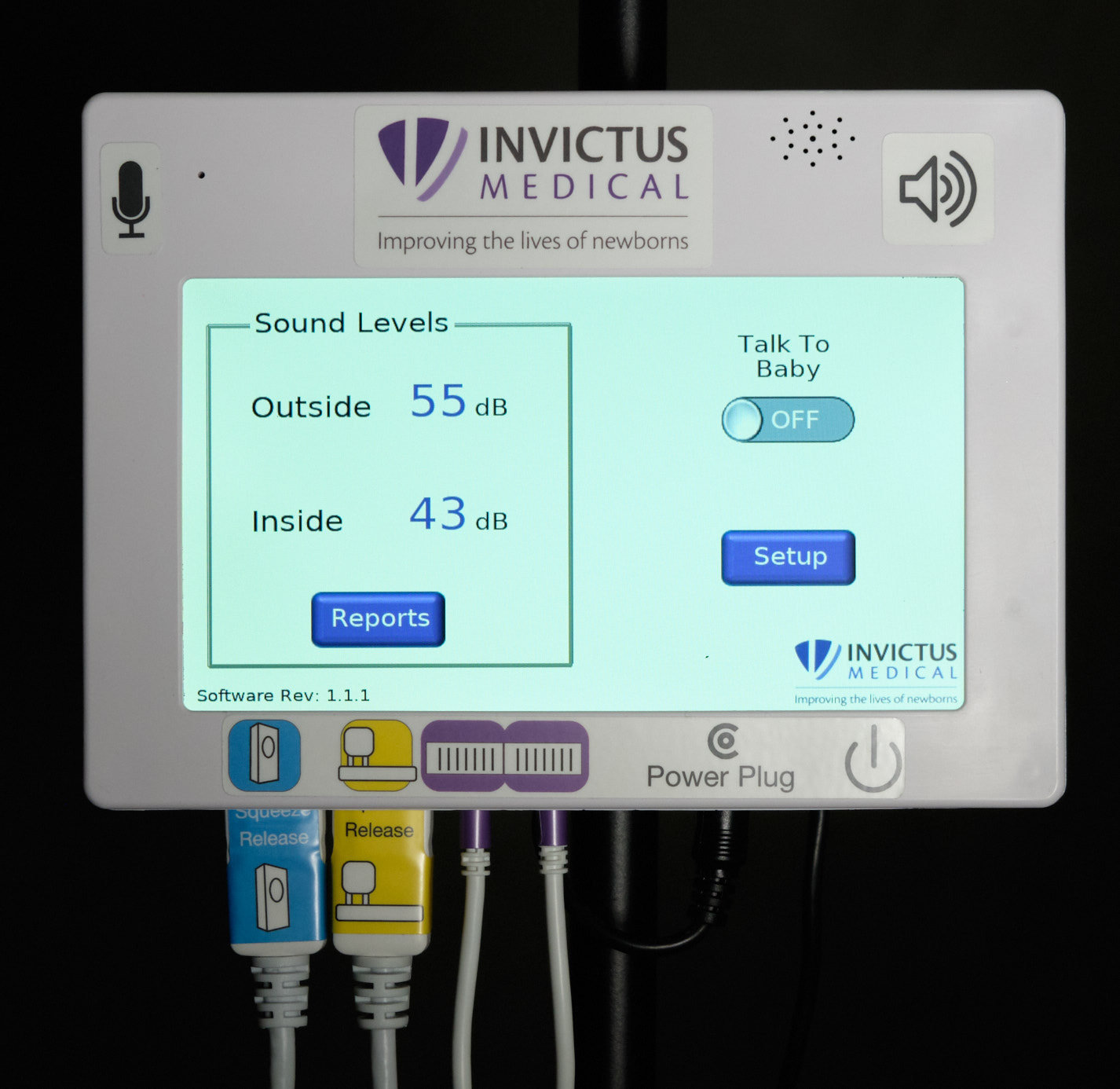 |
| Control unit front face and home screen |
 |
| Assembly of the pieces inside the incubator |
 |
| Outside noise sensor positioned on the outside of the incubator |
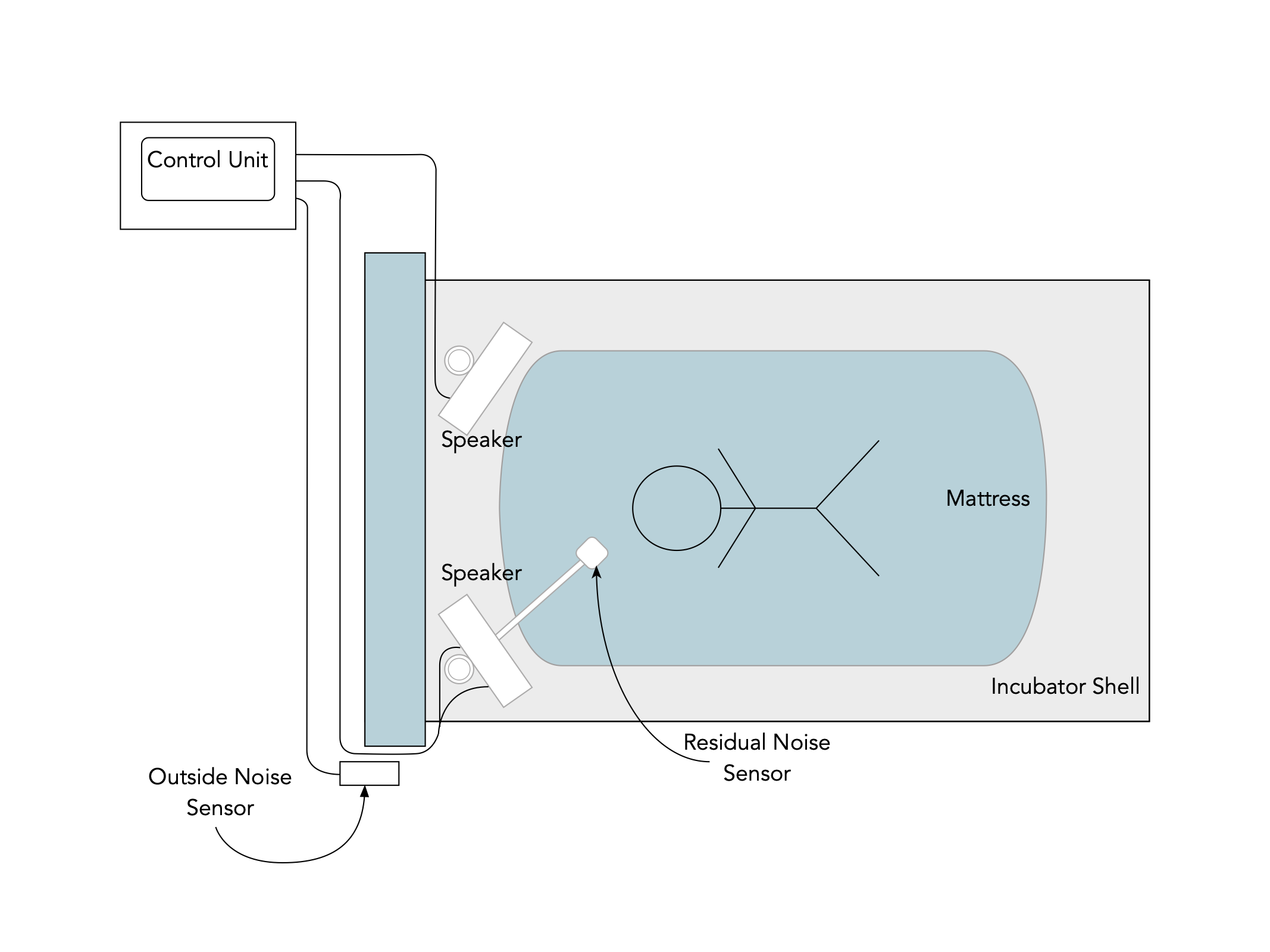 |
| Diagram of the assembled system |
Intellectual Property
Invictus is the assignee or has been exclusively licensed 12 issued patents, 11 of which have expiration dates between 2030 and 2040. These patents have claims generally directed towards safeguard techniques, hardware implementations, and other aspects active noise control.
Invictus has two pending application families.
FDA Status
Neoasis® has been cleared by the FDA for use in the NICU.
