Quotes From The Literature
 |
 |
 |
 |
NICU Noise Levels Exceed Guidelines
Noise levels in NICUs have been shown to be consistently louder than guidelines provided by the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP). These guidelines stipulate that the noise levels that the hospitalized infants are exposed to should not exceed 45 dB, A-weighted (dBA), averaged over one hour and the sound pressure level should not exceed 55 dBA for 10% of the measurement duration. Noise measured both inside and outside an incubator show guidelines are frequently exceeded throughout the day.
Effects Of NICU Noise On Sleep Hygiene And Weight Gain
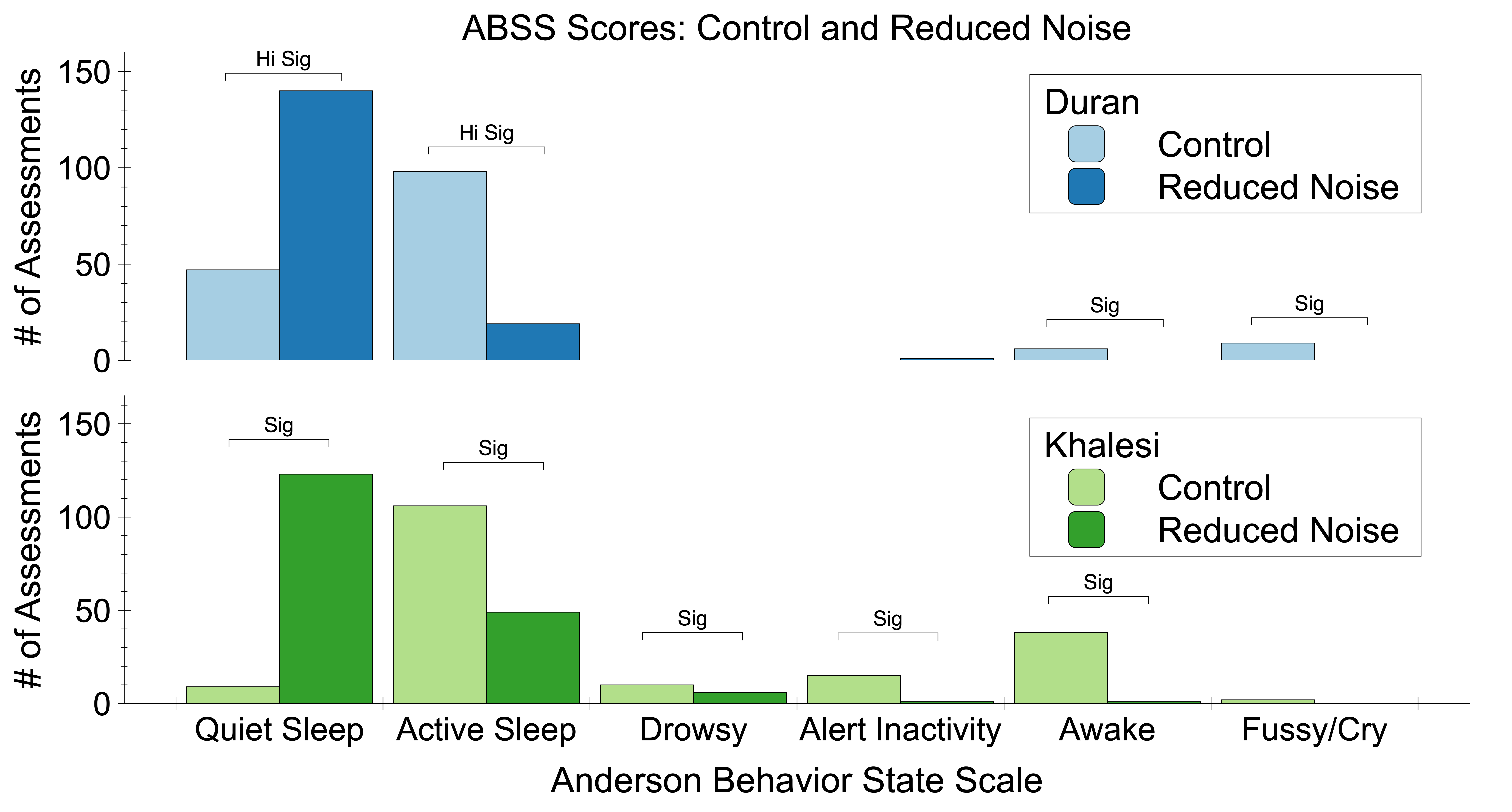
| Quieter environments can lead to better NICU sleep hygiene. In these two studies by Duran and Khalesi, the application of earmuffs adhered to infants’ heads resulted in a relative shift to quiet sleep from active sleep and less time awake. |
 |
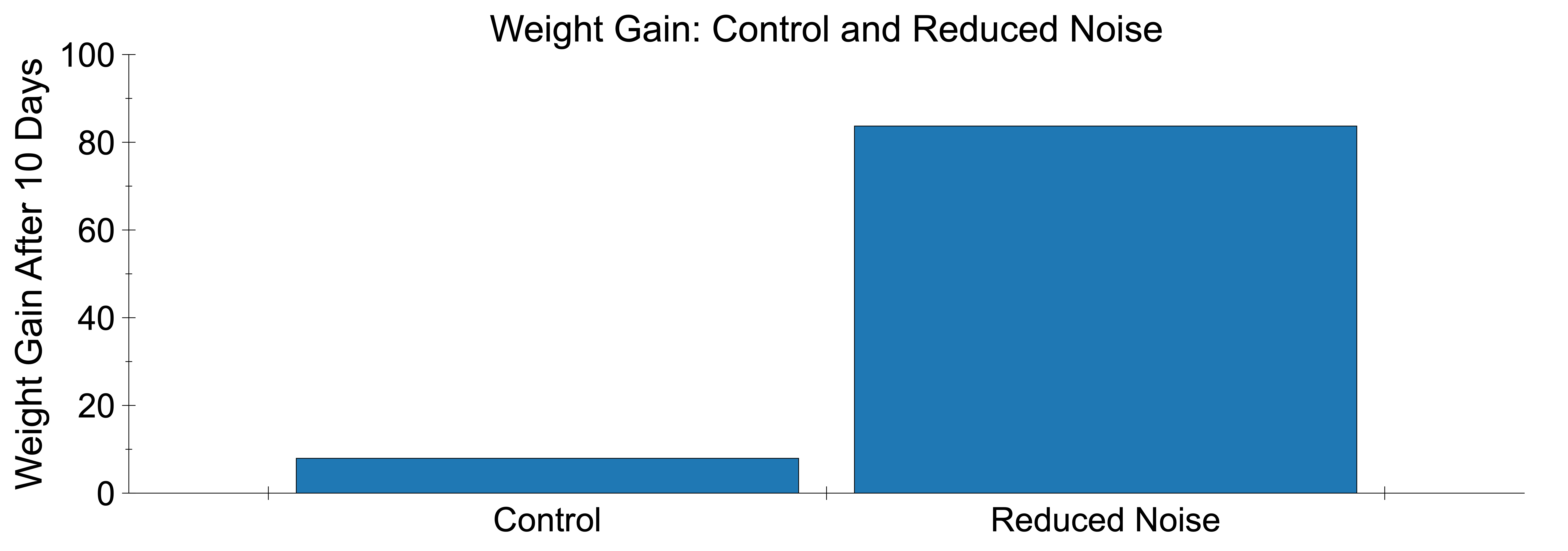
| Quieter environments can lead to better weight gain in the NICU. Abdeyazdan successfully detected changes in weight gain secondary to a change in the noise environment during a 10-day study. |
 |
Directed Communication
While excessive noise is shown to be detrimental to the well-being of the hospitalized infant, proper exposure to human voices, especially in directed communication between the infant and parents, is proving to be beneficial. A correlation exists between the amount of adult language the preterm infant is exposed to in the NICU and the amount of reciprocal vocalizations and meaningful early conversations. It was noted that hospitalized infants at 32 weeks were particularly devoid of exposure to human speech because they were “often still in an isolette [incubator], where it has been shown that little language is audible.” The long-term effects of this are marked. Analysis at 7- and 18-month post discharge shows a correlation between NICU voice exposure and scores in several types of cognitive and language scores.
Single Family Rooms
Single family rooms (SFR) have provided many improvements to the NICU experience, both for patients and their families. Sound levels in SFRs have been found to decrease very slightly though, given the life support equipment that’s still needed in the room. A comparison from the literature between different room types is shown here.
| Unit Type | Leq (dB) |
| Open unit (level 3) | 59 |
| SFR without vent support | 52 |
| SFR (level 3) with vent support | 53 |
| Unoccupied room | 38 |
| AAP Guidelines | 45 |
Other Approaches To Reduce Noise Are Ineffective
| Approach | Challenges Noted In Literature |
| NICU Reconstruction |
|
| Single Family Rooms |
|
| Staff Education |
|
| Light Warnings |
|
| Ear Coverings or Ear Plugs |
|
| Moderating Alarms |
|
| Blankets Covering Incubators |
|
